Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory condition where a collection of immune cells (granulomas) causes clumps of swollen tissue in an organ. Cardiac sarcoidosis occurs when this condition affects the heart, which can affect normal heart function.
Cardiac sarcoidosis is thought to occur in 25-30% of sarcoidosis patients. Some people may experience symptoms of cardiac sarcoidosis suddenly, which may include arrythmias, chest pain, shortness of breath, or, in serious cases, heart failure. It may also be detected incidentally in patients who already have a diagnosis of sarcoidosis. How the condition will affect a person varies.
The Royal Brompton Cardiac Sarcoidosis Service
Royal Brompton Hospital, part of Guys and St Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, is a tertiary cardiac and respiratory centre. We look after one of the largest cardiac sarcoidosis patient populations worldwide, with over 2000 patients under our care and over 250 new patient referrals a year from across the United Kingdom and internationally.
Our team of specialist consultants and nurses have accrued extensive experience in the management of cardiac sarcoidosis over the last 15 years. We have developed a multi-disciplinary approach by a number of specialists (cardiologists and sarcoidosis experts) for the diagnosis and management of cardiac sarcoidosis aiming to improve the accuracy and efficacy of our management.
When to suspect cardiac sarcoidosis
For patients who have a known diagnosis of sarcoidosis, clinical practice guidelines recommend reviewing a patient’s cardiac history, looking out for specific cardiac symptoms, and carrying out tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) or an echocardiography (echo). Abnormal tests results on an ECG or an Echo are usually followed up by further tests, such as a cardiac MRI.
Clinicians might also want to suspect cardiac sarcoidosis in an otherwise healthy person with new-onset advanced heart block (atrioventricular or AV block), ventricular arrhythmias or unexplained heart failure. Cardiac sarcoidosis can also mimic other cardiomyopathies, which can pose challenges in accurate diagnosis.
Cardiac sarcoidosis remains a key cause of sudden cardiac death in young patients, which can be preventable. Early and accurate diagnosis, as well as timely treatment and follow up, are vital for the effective management of this condition.
Diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis
The clinical team at Royal Brompton Hospital uses a multidisciplinary (MDT) approach to help reach a confident diagnosis of cardiac sarcoidosis.
Our MDT meeting involves a range of experts from the clinical team who will come together to review each patient case to determine the likelihood of a cardiac sarcoidosis diagnosis, and the most appropriate management strategy.
The diagram below shows our typical MDT approach from the point of receiving a new referral. The outcome of the MDT meeting, including diagnosis and treatments, are discussed with the patient, and with the referring hospital clinician and the patient’s GP, to ensure that treatment plans can be instigated.
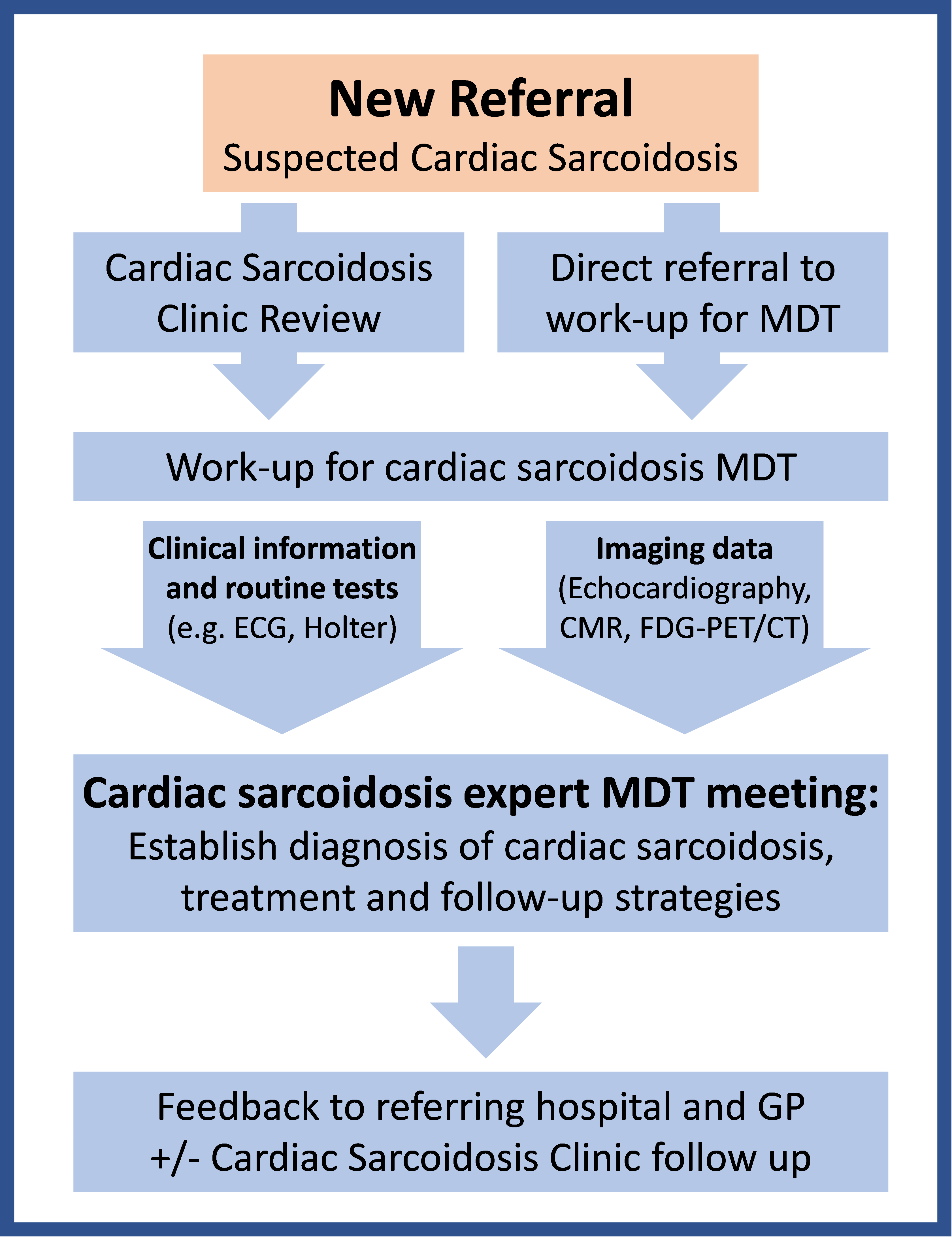
The cardiac sarcoidosis clinic
The cardiac sarcoidosis clinic is run as a combined clinic of respiratory physicians and cardiologists, led by experts in the field of sarcoidosis.
During the clinic appointment, patients are either assessed as part of a work-up for discussion at the cardiac sarcoidosis MDT meeting to establish the diagnosis and treatment strategies, or as part of clinical follow up and assessed for further management.
A comprehensive assessment is performed, which may include:
- A clinical assessment with the cardiac sarcoidosis team, which usually includes both a consultant cardiologist and a respiratory consultant.
- Tests such as blood tests, chest CT scans (if not performed recently), lung function tests, an electrocardiogram, and an echocardiogram
- Advanced imaging tests may also be carried out, such as CMR (a non-invasive assessment of heart function, oedema and scar) or FDG-PET/CT (a non-invasive assessment of inflammation)
Cases involving cardiac sarcoidosis patients who continue to experience clinical challenges, such as persistent arrythmias or inflammation, despite management/treatment can also be discussed in the multidisciplinary meeting.
Ongoing follow up is arranged in regular cardiac sarcoidosis clinics. We believe it is essential that patients and families understand our treatment plans. Therefore, we aim to discuss these in detail in clinic.
Experts in cardiac sarcoidosis
Our team of experienced chest physicians and cardiologists are international experts in the field of cardiac sarcoidosis and provide a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary approach, using advanced imaging tests to provide a diagnosis and treatment plan.
- Professor Athol Wells, consultant respiratory physician and respiratory lead for the cardiac sarcoidosis service
- Dr Rakesh Sharma, consultant cardiologist and cardiology lead for the cardiac sarcoidosis service
- Dr Vasileios Kouranos, consultant respiratory physician
- Dr John Baksi, consultant cardiologist and cardiac MRI expert
- Dr Raj Khattar, consultant cardiologist and echocardiography lead
- Dr Kshama Wechalekar, consultant in nuclear medicine
- Ms Sue Gilmour, specialist cardiac sarcoidosis and heart failure nurse
Appointments
We always try and see patients as quickly as possible after they have been referred. Download the referral form.
We can usually see clinically urgent cases within 2 weeks.
We can arrange day-case visits for patients who live far away (so all tests can be performed on the same day).
Contact details
If you are a health professional and have any questions about cardiac sarcoidosis or the referral process, please contact Vasileios Kouranos on 020 7351 8742.
You can also contact the cardiac sarcoidosis clinic administrator:
Sue Lawlor
- Email: S.Lawlor@rbht.nhs.uk
- Telephone: 020 7352 8121, ext: 82060
